How to use Elastic automatic module¶
Calculate Elastic constants from scratch using a structure file¶
Initiate ‘Elastic’ module: ‘Elastic’ module can be initiated from CASCADE toolbar by clicking XXX icon.

Fig. 155 Invoke ‘Elastic’ module.¶
Name ‘Elastic’ module: To start from a structure file, corresponding option has to be selected. If before performing the calculation for elastic constants, structure is to be relaxed option to relax the structure has to be checked.
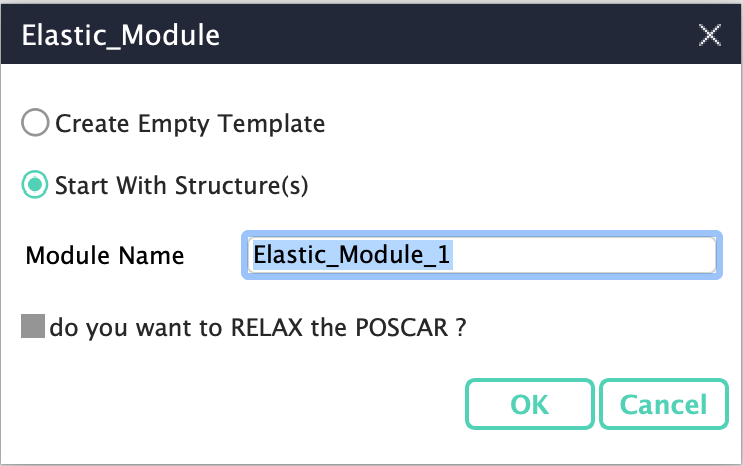
Fig. 156 Name the ‘Elastic’ module and select other options.¶
Browse a supported structure file: At the next step, a structure file in a format supported by CINEMAS is to be browsed. CINEMAS in its current version supports \(\texttt{POSCAR/*.vasp/*.cif/*.in/*.xsf}\) formats.
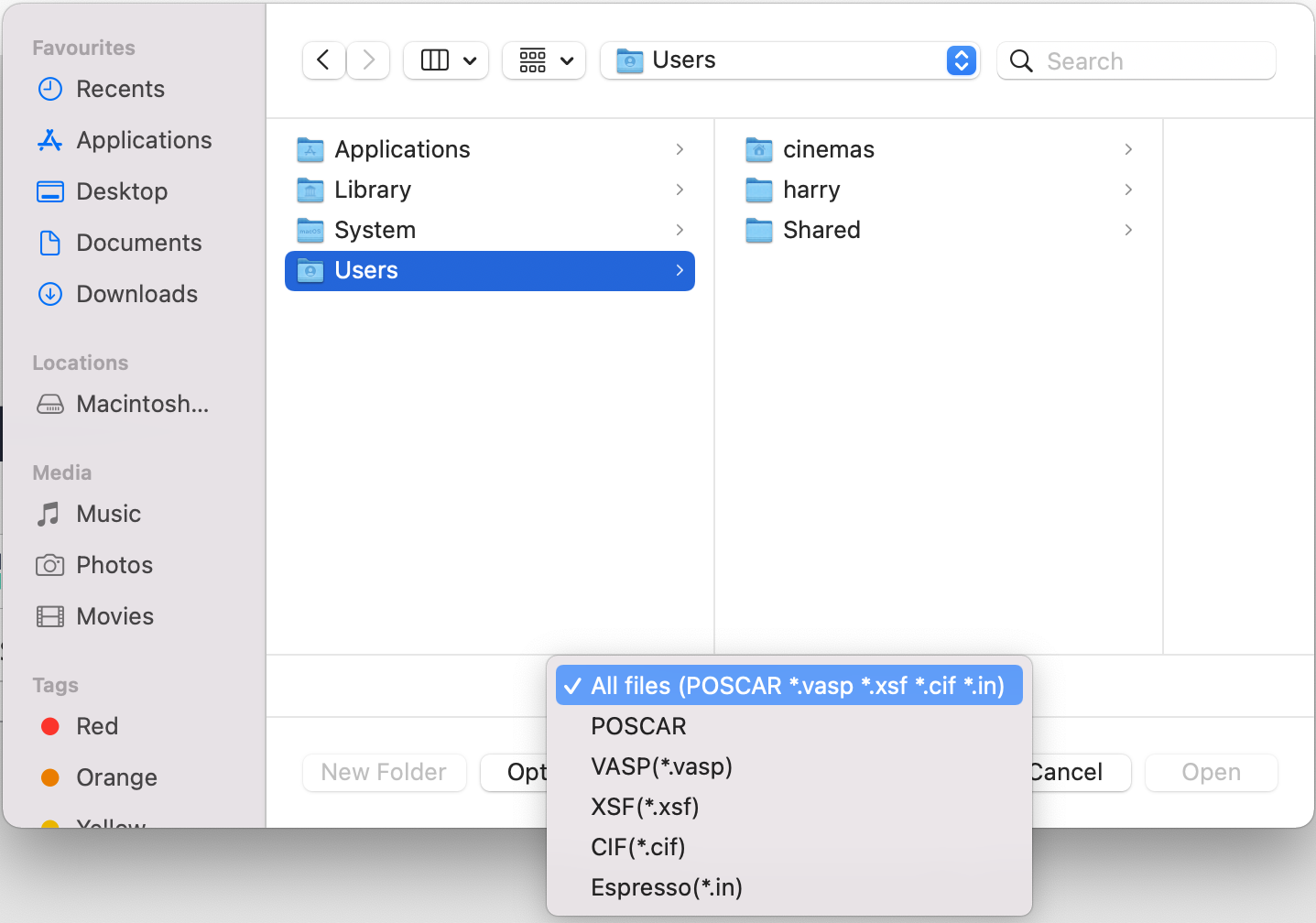
Fig. 157 Browse a structure file from the disk.¶
Settings for the calculation(s): Next, a dialog box is popped up showing default settings, the user can either accept these by clicking ‘OK’ button or make their settings in ‘user settings’ mode as shown in the Fig. 158
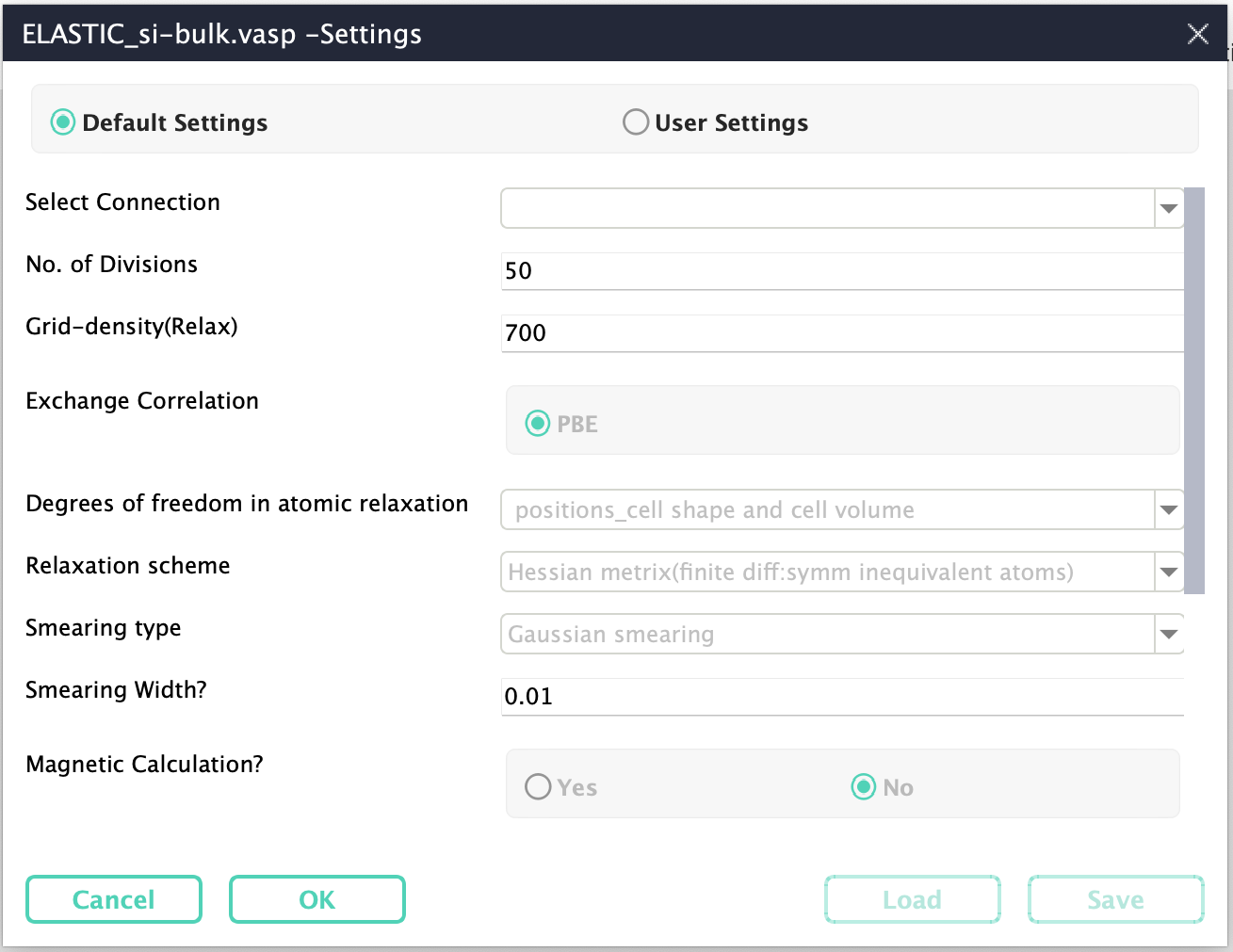
Fig. 158 Accept default settings, or make specific settings.¶
Creation of workflows: At the next step, immediately a workflow is created with a single calculation if ‘relax’ option is not selected. Or a parent-child workflow with two calculations is created, one for relaxation of the structure and the other to compute the elastic constants. See Fig. 159
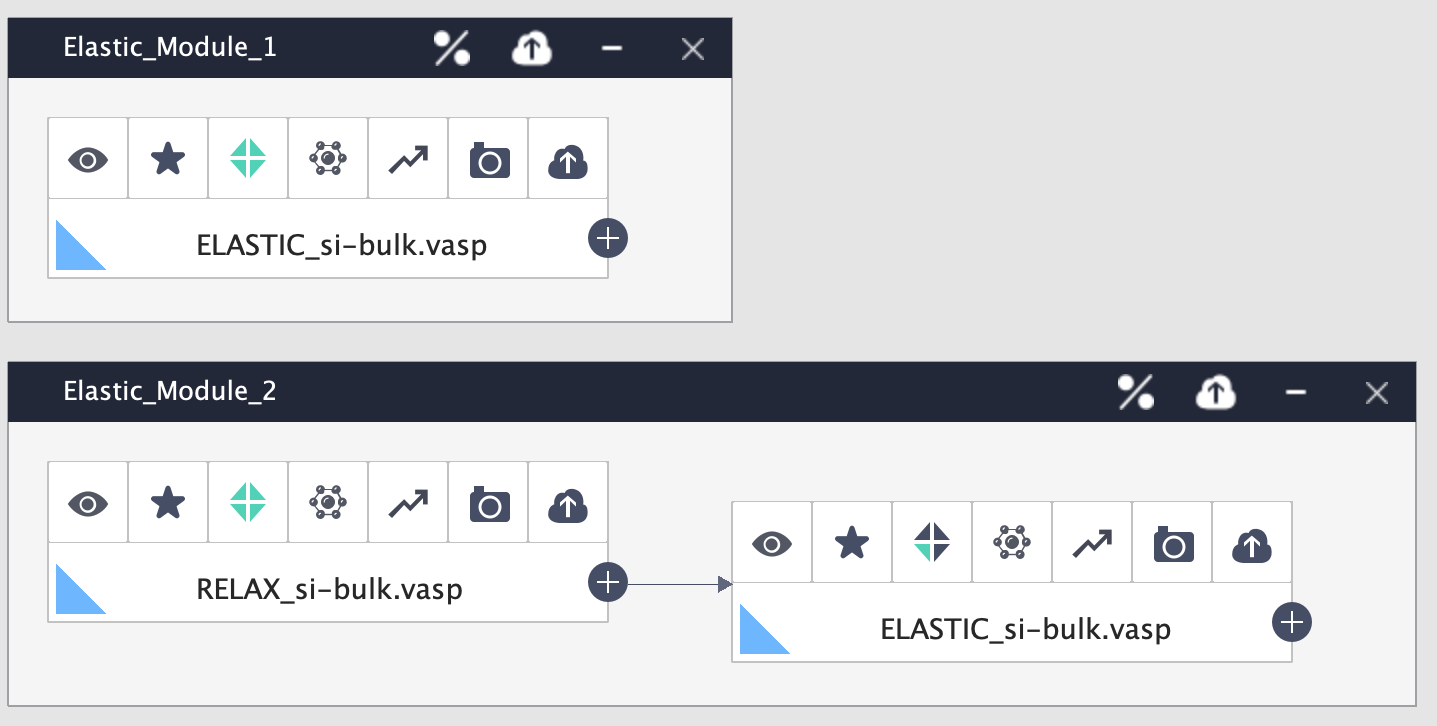
Fig. 159 Creation of workflows.¶
Submission on compute server: The workflow, as mentioned above is created and submitted to a chosen compute server at the same time without any user intervention. User can track the progress of the computation in the ‘queue’ workspace.
Automatic download of output files: Once the computation is over for VASP code, OSZICAR and OUTCAR files are downloaded automatically. As these file are required to obtain information about iterations and elastic tensor, respectively.
Post-processing and extraction of elastic constants: With a single click on the % icon on the module window, several elastic constants are displayed as shown in the Fig. 160. We acknowledge the use of Pymatgen library for parsing and extraction of the elastic constants.
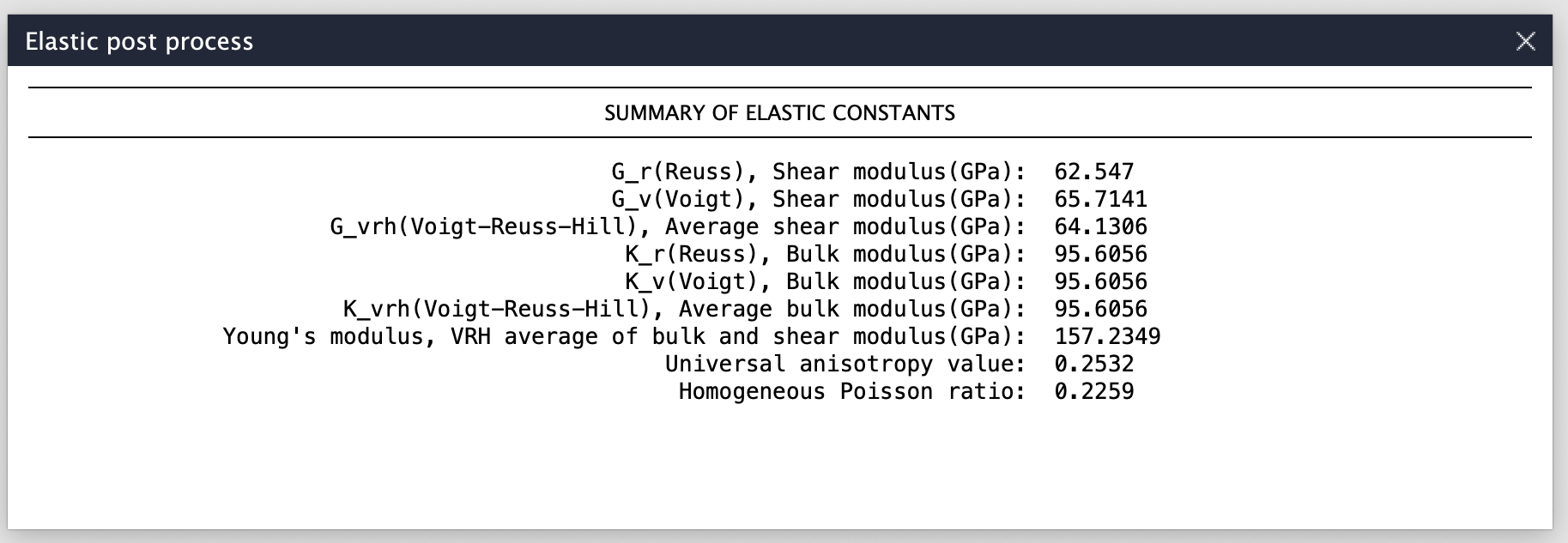
Fig. 160 Post processing of the calculation and extraction of elastic constants.¶
You can find a tutorial below explaining the functioning of Elastic module in CINEMAS.